5 Key Nursing Diagnoses
1. Decreased Cardiac Output
2. Ineffective tissue perfusion (renal)
3. Excess fluid volume related to kidney disease
4. Impaired Urinary Elimination r/t effects of disease, need for dialysis
5. Acute pain
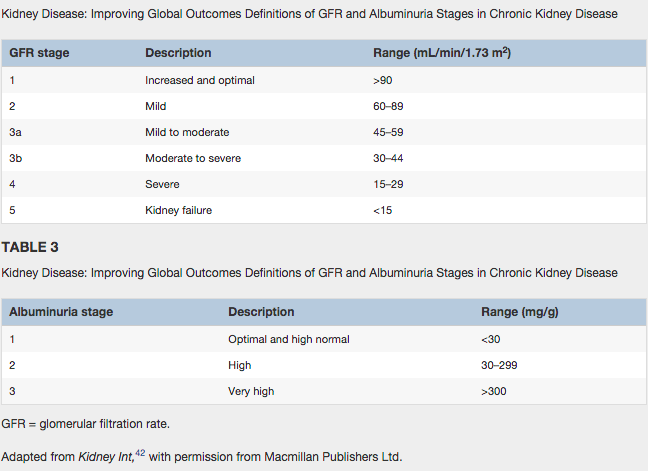
There will be excess fluid volume of fluid overload related to decrease glomerular filtration rate and sodium retention due to kidney malfunction. The glomerular filtration rate will be very low creating a lot of pressure on the kidneys. This will make it difficult for the patient to excrete urine. Furthermore, with excess fluid can not leave, so it overloads the lymph system. This can cause the following in the interstitial spaces: edema, weight gain, pulmonary congestion, hypertension, shortness of breath, dyspnea on exertion, oliguria (low output of urine) and altered mental status. The kidneys are already under pressure, but it will get increasing worse. There will be a electrolyte unbalance especially in sodium and potassium. Electrolytes like sodium and potassium regulates blood pressure, blood volume, and cardiac contractions. This can lead to decrease caridac output, or your heart unable to pump blood with oxygen throughout the body. The blood pressure will spike up because it is trying to compensate. This of course affects how well your blood is perfuse in the body if it still contains waste. It will also lead to decrease urine output, and if the body can not filter and remove its waste, then it can lead to kidney failure and dialysis.
Citations:
Ackley, B. (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care(9th ed.). Maryland Heights, Mo.: Mosby.
Lewis, S. (2011). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems. (8th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Elsevier/Mosby.
Ackley, B. (2010). Nursing diagnosis handbook: An evidence-based guide to planning care(9th ed.). Maryland Heights, Mo.: Mosby.
Lewis, S. (2011). Medical-surgical nursing: Assessment and management of clinical problems. (8th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Elsevier/Mosby.